4. Summary of delivered product
4.1 Overview
The current GovERP solution serves as an initial framework aimed at establishing the groundwork for future enhancements and deployments. The current solution was paused mid-flight in November 2023, and hence a number of capabilities are still under development, and all testing
was not completed.
Figure 9 provides an overview of the build completeness of the MVP1.1 build in terms of both value stream and functional capability.
Note, no System Integration Testing (SIT) or User Acceptance Testing (UAT) occurred as part of GovERP.
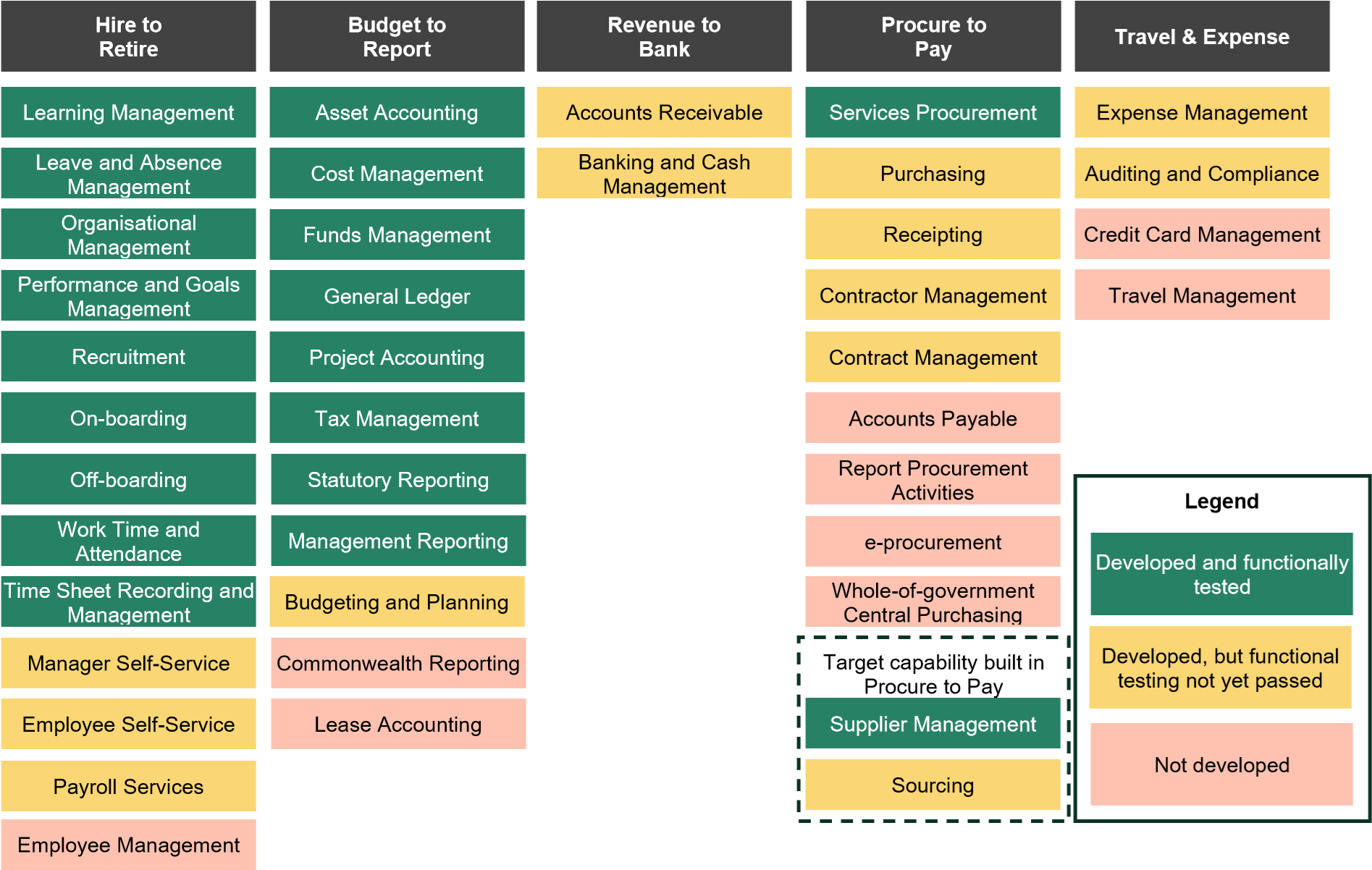
The table below summarises the current capability status within the value streams.
| Value stream | Full GovERP Solution coverage | MVP1.1 solution coverage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Built | Planned | Built | Planned | |
| Hire to Retire (H2R) | 9 | 22 | 9 | 13 |
| Finance, including Revenue to Bank (R2B) and Budget to Report (B2R) | 8 | 15 | 8 | 13 |
| Procure-to-pay (P2P) | 2 | 13 | 1 (see Table note 1) | 9 |
| Travel and expense management (TEMS) | 0 | 4 | 0 (see Table note 2) | 4 |
| Total | 19 | 54 | 18 | 39 |
Table note 1: “Supplier Management” was not in scope of MVP1.1. However, Services Australia built and functionally tested this capability.
Table note 2: The vendor, 8common, advised all build elements were completed and tested, however, these were not integrated by Services Australia as part of the GovERP solution.
In respect of the above value streams, a total of 167 WRICEFs were identified as part of this assessment, of which 13 relate to AGD.
4.2 Functions and capability
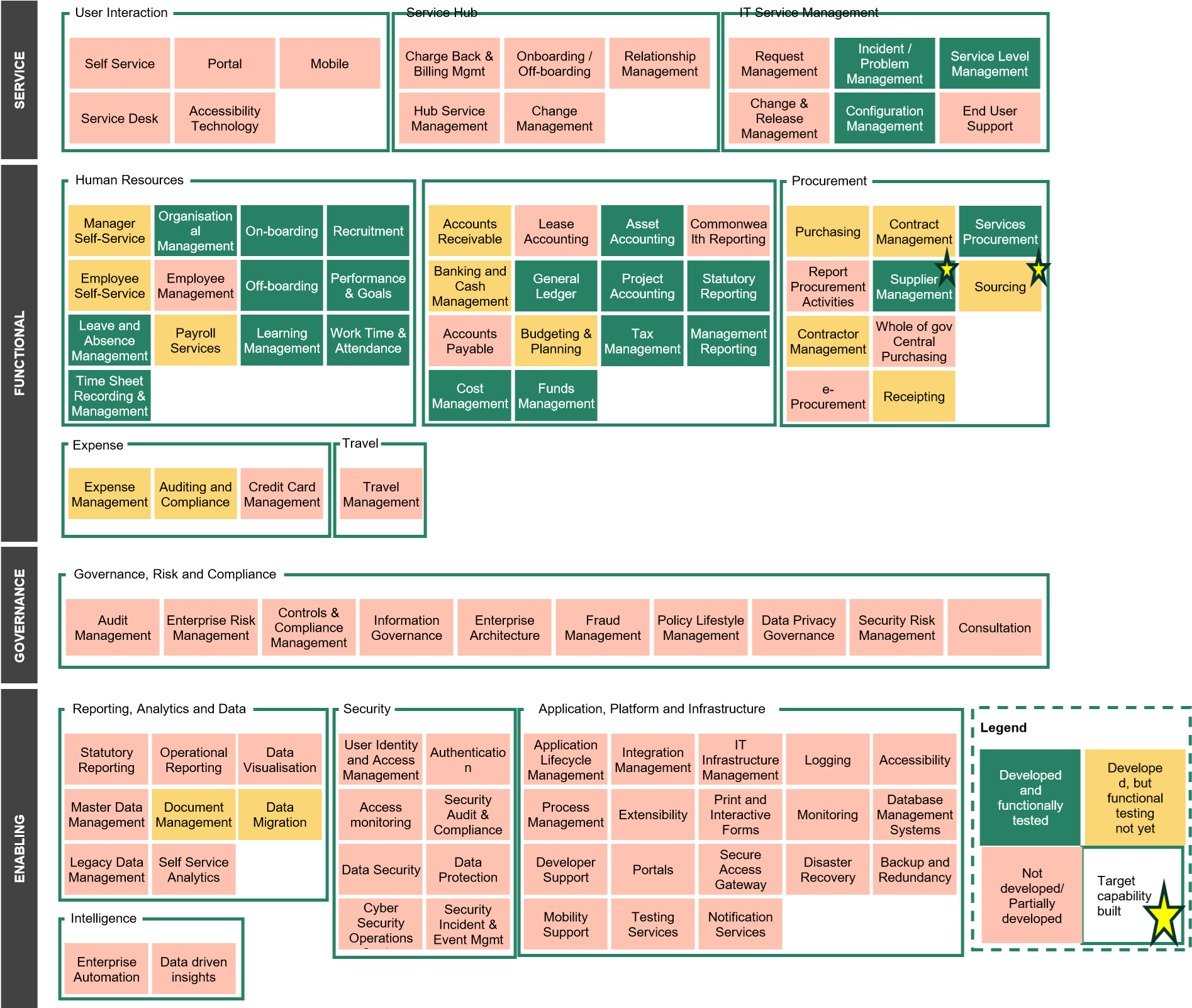
Further to the Value Stream view provided in Section 4.1, below is the current build completeness of each capability within GovERP.
The status provided aligns with the information communicated by Services Australia (see Reference 1). Appendix C provides details on the intended contents of each component box.
Engagement with stakeholders identified the need for enhancements to meet the specific requirements of other entities. Anecdotally, this was always expected within the GovERP intended operating model, prior to project’s pause. For example, additional changes to MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements were identified to address the needs and scenarios of AGD, particularly in areas such as recruitment, learning management, finance and procurement.
Further insights into the build status of each of the Value Streams is discussed in the subsequent sections.
4.3 Hire to Retire (H2R)
Human Capital Management (HCM) refers to the software and systems designed to manage and optimise the Human Resources (HR) business area of an organisation within the broader framework of an ERP system.
Within GovERP, the HCM functionality is encapsulated within the Hire to Retire (H2R) value stream, implemented through SAP’s SuccessFactors technology.
The H2R value stream manages and supports the course of an individual’s career within the APS, including recruitment, onboarding, mobility, pay, performance management, development, workforce management, retentions, and separation activities.
The H2R platform, SuccessFactors, is hosted on the SAP Sovereign Cloud as a SaaS (see Reference 2). The current state solution is available in a development tenant and all template features are enabled (see Reference 3).
4.3.1 Build status across value streams, functions, and components
A total of 124 business processes, across 22 capabilities were presented to the Business Process Management Council (BPMC) and subsequently endorsed (see Reference 4).
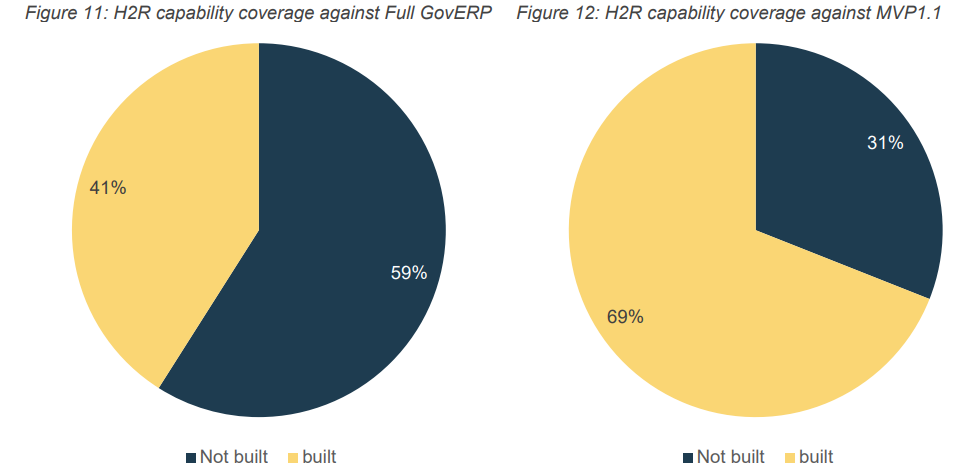
Figure 12: H2R capability coverage against MVP1.1
Table 5 outlines the status of H2R capabilities, detailing completion, associated technologies, and any notable exceptions.
| Capabilities | Scope | Build Complete? (see Reference 6) | Business Process | Technology component | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 12 | SuccessFactors Learning Management | |
| Leave And Absence Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 5 | SuccessFactors Employee Central Time off – Leave management | |
| Organisational Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 5 | SuccessFactors Employee Central – Core HR | |
| Performance and Goals Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 4 | SuccessFactors Performance and Goals | |
| Recruitment | MVP1.1 | Yes | 9 | SuccessFactors Recruitment and Onboarding 2.0 | |
| On-boarding | MVP1.1 | Yes | 7 | SuccessFactors Recruitment and Onboarding 2.0 | |
| Off-boarding | MVP1.1 | Yes | 5 | SuccessFactors Recruitment and Onboarding 2.0 | |
| Work Time and Attendance | MVP1.1 | Yes | 3 | SuccessFactors Employee Central – Time Tracking – Time and attendance | |
| Time Sheet Recording and Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 2 | SuccessFactors | |
| Manager Self Service | MVP1.1 | No | 3 | SuccessFactors | Build and functional testing considered incomplete given overall build status of H2R. Note, “Built, but functional testing not yet passed” (i.e. “No” for Completeness result) included as the rating for this capability to reflect the build status of many dependent capabilities. |
| Employee Self Service | MVP1.1 | No | 2 | SuccessFactors | Build and functional testing considered incomplete given overall build status of H2R. Note, “Built, but functional testing not yet passed” (i.e. “No” for Completeness result) included as the rating for this capability to reflect the build status of many dependent capabilities. |
| Payroll Services | MVP1.1 | No | 15 | SuccessFactors Employee Central Payroll | Defect in the Manage Salary Recall process, requiring a manual step to recall the bank file. This issue, alongside remaining test scenarios, is affected by open defects from RBA testing. |
| Employee Management | MVP1.1 | No | 8 | SuccessFactors Employee Central – Core HR SuccessFactors Integration Centre SAP Analytics Cloud with IAS SAP Cloud Platform Integration | Build and functional testing not completed for Manage APSED Report |
| Compensation Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 7 | SuccessFactors | |
| Concurrent Employment | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 1 | SuccessFactors | Services Australia advised this was built, however, could not provide evidence of this functionality |
| Global Employment | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 3 | SuccessFactors | |
| HR Case Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 2 | SuccessFactors | |
| Schedule Rostering | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 2 | SuccessFactors | |
| Succession and Career Development | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 5 | SuccessFactors | |
| Work Health and Safety | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 11 | SuccessFactors | |
| Workforce Relations | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 5 | SuccessFactors | |
| Workforce Planning | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 7 | SuccessFactors |
4.3.2 H2R WRICEF summary (see Reference 7)
Changes from the ‘out-of-the-box’ product within GovERP services are quantified using WRICEF components (workflows, reports, interfaces, conversions, enhancements, and forms). Table 6 below provides a summary of these WRICEF’s in H2R for MVP1.1.
| Capability | Workflows | Report | Interfaces+ Integration | Conversion | Enhancement | Form | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Payroll Services | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 10 | ||
| Employee Management | 1 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Leave Management | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Organisational Management | 1 | 1 | |||||
Time & Attendance | 1 | 1 | |||||
| TOTAL | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 18 |
A further three interfaces were planned for MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements (two for Employee Management and one for Organisational Management).
Regarding the build status of the above WRICEF’s, all have been built for MVP1.1. (see Reference 9)
The complexity of managing the MVP1.1 WRICEFs on an ongoing basis is summarised below. Appendix D details a breakdown of each WRICEF and the indicative effort required for maintenance.
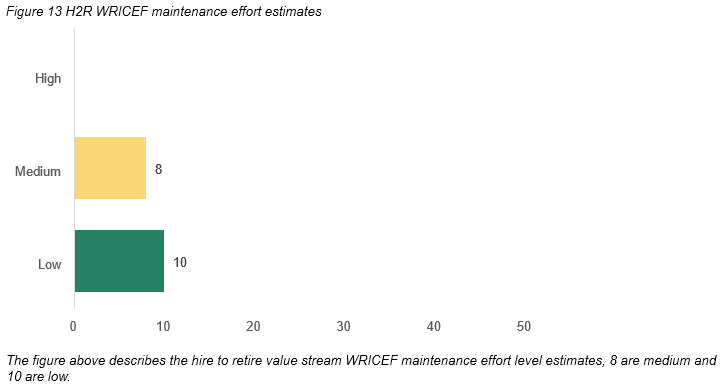
The ongoing impact of maintaining these WRICEF’s will depend on the updates and releases by SAP. SuccessFactors follows a semi-annual (6-monthly) release cadence.
The H2R value stream maintains close integration with SAP S/4HANA Finance for Financial processes and Travel and Expense Management systems for employee expenses. When considering the reuse of H2R capabilities, it is crucial to assess the integration landscape and dependencies between the H2R value stream and these other systems.
Discussions with SAP revealed the existing SAP build is intricately integrated across various products. While this facilitates data flow and operational continuity, it needs close consideration when entities are determining reuse deployment options.
Effort will be necessary to disentangle SAP SuccessFactors and SAP S/4HANA, to enable progressive deployment of the technologies or a different combination of technologies, such as deploying on the SAP Sovereign Cloud.
In addition, nine ServiceNow integrations were established with SuccessFactors (see Reference 10):
- Business Unit
- Company
- Department
- Division
- Employee
- Location
- Section
- Team Unit
- Cost Centre.
These could be repurposed to other IT Service Management tools to enable integration into other entities technology landscapes.
4.3.3 Key H2R insights
The key insights for H2R are summarised in Table 7 below:
| H2R insights |
|---|
| H2R1 For an agency that has a large IT support team, ongoing management and upgrade of this solution would be achievable. For smaller entities, closer consideration would need to be given to maintenance implications |
| H2R2 The whole of government GovERP template has not been updated for the new whole of government common conditions. |
| H2R3 A number of the WRCIEF enhancements that were implemented were required to make the system suitable for public sector use |
| H2R4 While the solution offers comprehensive HR management capabilities, and a lot of reporting capability out-ofthe-box, in-depth analytics and reporting is not fully provisioned. |
| H2R5 To enable shared services, data separation on the same tenant would need to be built and tested |
| H2R6 For ongoing use, application regression testing, and any resolution of defects, or resolution of custom or enhanced codes, will be the responsibility of the customer to manage, not the vendor. There will be at least two application upgrades a year. |
| H2R7 There are 18 H2R WRICEF’s, most of which will require effort to maintain. |
| H2R8 Advice has been provided from Services Australia, that ‘Manage APSED Report’ is the only sub-component within Employee Management outstanding in the build. Similarly, within Payroll Services, only ‘Manage Salary Recall’ has not passed functional testing. |
| H2R9 The existence of WRICEF components highlights the importance of considering the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of H2R capabilities in GovERP. |
| H2R10 If entities only want to use specific capabilities, or any part of the solution stack, then an appropriate commercial construct would likely be required at a whole of government level. |
| H2R11 MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements already sits on top of MVP1.1. The solution is now ageing. Further delays of how to use this platform will put the re-use agenda further out of reach for ERP. |
| H2R12 A whole of government standard could be set on how vendors need to operate with the APS in order to deliver on ERP services. This would greatly increase the chance of interoperability and re-use in the eco-system. |
4.3.4 Re-use considerations for H2R
In accordance with the re-use hierarchy (see Reference 11), each capability within H2R has been assessed for its potential for re-use. Below is a summary of this assessment.
From a Tier 3 intellectual property re-use perspective, almost all information could be considered by another agency.
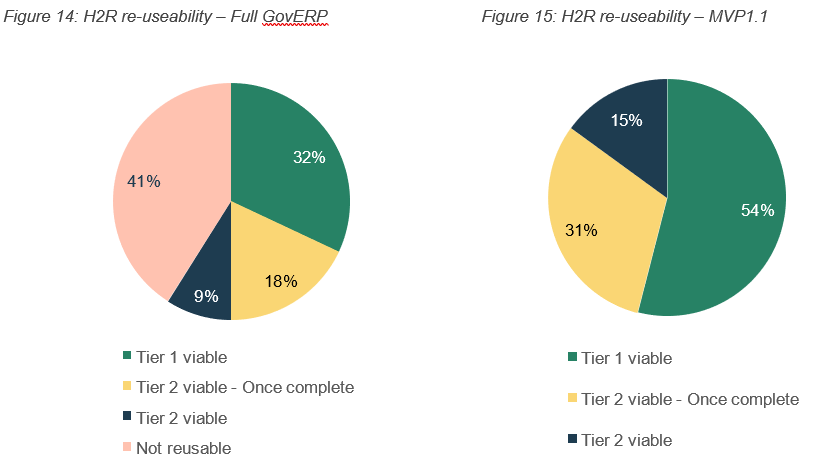
Figure 15: H2R re-useability – MVP1.1
Table 8 details each capability, and the potential for re-use, along with the implications of doing so. Refer to section 5.2 for the adoption considerations for any other agency, which outlines the effort and other considerations involved.
Capabilities | Technology | Re-Use Potential | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Offboarding | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Performance And Goals Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Recruitment | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Onboarding | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Work And Time Attendance | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Time Sheet Recording and Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 1 | Commercial implications / changes required |
| Leave And Absence Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Organisational Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Employee Management | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 – If completed | Maintenance Implications |
| Payroll Services | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 – If completed | Maintenance Implications |
| Employee Self Service | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 – If completed | Maintenance Implications |
| Manager Self Service | SuccessFactors | Viable – Tier 2 – If completed | Maintenance Implications |
| Compensation Management | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Concurrent Employment | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Global Employment | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| HR Case Management | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Schedule Rostering | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Succession and Career Development | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Work Health and Safety | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Workforce Planning | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
| Workforce Relations | TBD – Not progressed | Not Viable | Not Built |
Whilst the table above indicates differing levels of capability reuse potential, note that Section 5 considers the pragmatic means through which an entity could consider deploying these capabilities.
4.4 Finance – Budget to Report (B2R) and Revenue to Bank (R2B)
Finance includes two value streams which are:
- Budget to Report (B2R): Includes the activities undertaken to planning and budgeting, cost and funds management, asset management and organisational activity reporting.
- Revenue to Bank (R2B): Includes the activities undertaken to receipt and bank cash, including accounts receivable, banking and cash management.
These value streams are enabled through the Financial Management Information System (FMIS). The FMIS encompasses the software and systems aimed at managing and optimising the Finance business area within an organisations ERP framework. In GovERP, the FMIS functionality is implemented through the on-prem version of SAP’s S/4HANA technology, hosted on Services Australia’s private Microsoft Azure cloud tenancy (see Reference 12).
4.4.1 Build status across value streams, functions, and components
A total of 166 (see Reference 13) Finance business processes across 16 capabilities were presented to the BPMC, and 103 were endorsed (see Reference 14). The remaining 63 not endorsed processes cover accounts payable, reporting, budgeting and planning, and lease accounting. To continue to progress the build of GovERP, Services Australia commenced the build of all Finance processes, including those not yet endorsed.
The build completion across Finance for MVP1.1 is depicted in the figure below.
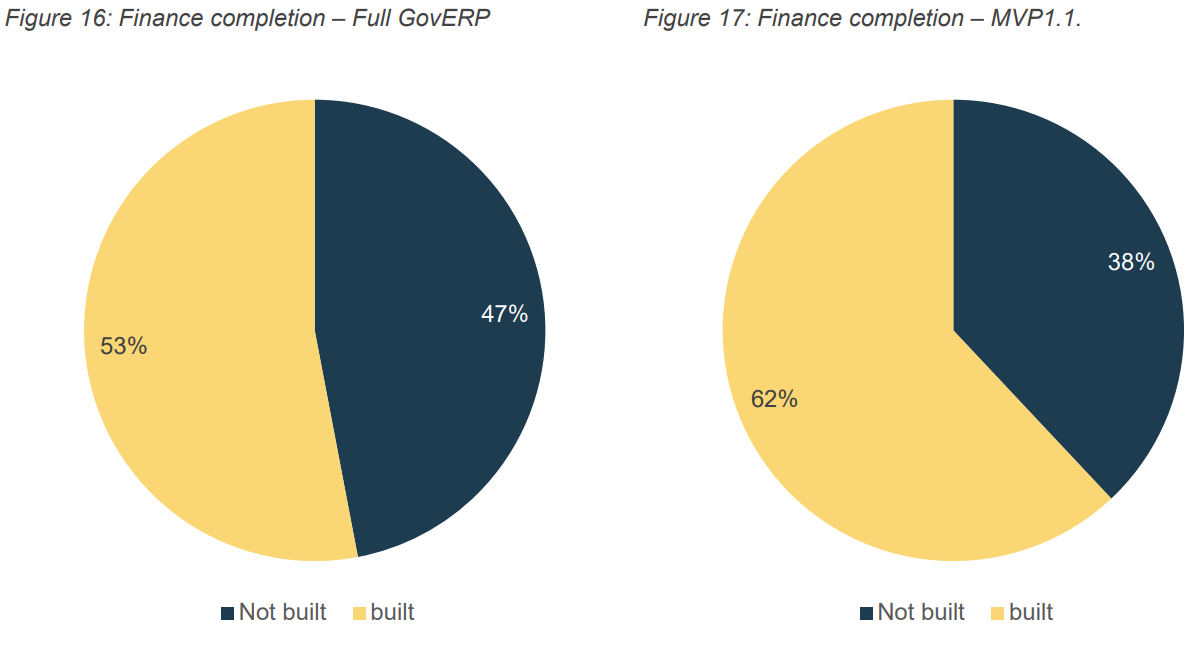
Figure 17: Finance completion – MVP1.1
Further granularity is provided below for the respective value streams within Finance.
4.4.2 Budget to Report (B2R)
The build completion for the B2R value stream across the GovERP MVP and the full GovERP is depicted in the figures below.
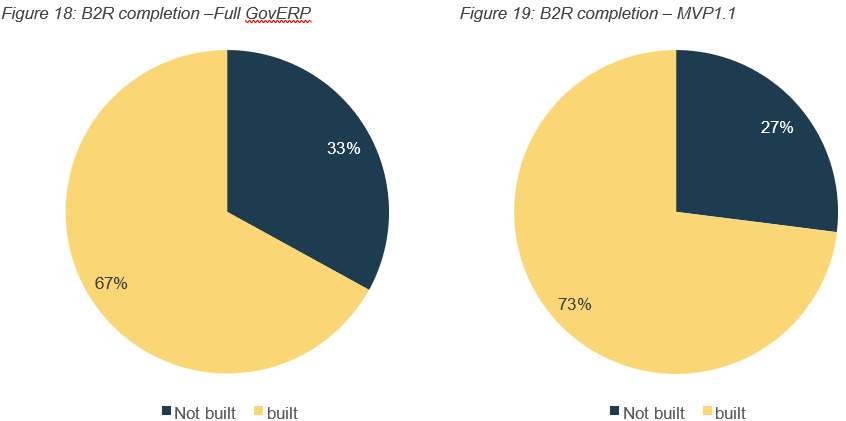
Figure 19: B2R completion – MVP1.1
The table below provides a detailed view of the build and testing status of respective capabilities.
| Capabilities | Scope | Build Complete? (see Reference 16) | Business processes | Technology component | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Accounting | MVP1.1 | Yes | 6 | SAP S/4HANA Asset Accounting RE-FX-LA CLM (Contract and Lease Management) | |
| Cost Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 6 | SAP S/4HANA Cost Management (Overhead Accounting) SAP S/4HANA Master Data Governance Central SAP S/4HANA Master Data Governance Embedded SAP Cloud Platform Integration | |
| Funds Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 3 | SAP S/4HANA Funds Management SAP Public Sector Management PSM_FM_CI_4 - PSM, Funds Management 4 PSM_MM_MAA - PSM, MAA Final Acct Assignment RE_FM_EARMARKED_FUND - RE/FM Earmarked Funds | |
| General Ledger | MVP1.1 | Yes | 7 | SAP S/4HANA General Ledger SAP S/4HANA Financial Closing Cockpit SAP S/4HANA Master Data Governance Central SAP Cloud Platform Integration | |
| Project Accounting | MVP1.1 | Yes | 6 | SAP S/4HANA Project Accounting SAP Analytics Cloud Planning SAP Cloud Platform Integration | |
| Tax Management | MVP1.1 | Yes | 2 | SAP S/4HANA Tax Management – Advanced Compliance Reporting (Basic Version) | |
| Statutory Reporting (see Reference 17) | MVP1.1 | Yes | 1 | SAP Analytics Cloud Analytics | |
| Management Reporting (see Reference 18) | MVP1.1 | Yes | 1 | SAP Analytics Cloud Analytics | |
| Budgeting and Planning | MVP1.1 | No | 6 | SAP Analytics Cloud Planning – Budgeting and Planning SAP Analytics Cloud Analytics | Manage external budget, as testing for integration with the Commonwealth Budget Management System (CBMS) could not be undertaken |
| Commonwealth reporting | MVP1.1 | No | 1 | SAP Analytics Cloud Analytics | Build not complete |
| Lease Accounting | MVP1.1 | No | 6 | SAP S/4HANA | No build information provided |
| Inventory Accounting | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 3 | SAP S/4HANA |
4.4.3 B2R WRICEF summary
Changes from the ‘out-of-the-box’ product within GovERP services are quantified using WRICEF components. The table below provides a summary of these WRICEF’s in B2R for MVP1.1.
| Capability | Workflows | Report | Interfaces+ Integration | Conversion | Enhancement | Form | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | 2 | 2 | |||||
| Asset Accounting | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |||
| Budget & Planning | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Cost Management | 4 | 2 | 6 | ||||
| Funds Management | 3 | 5 | 8 | ||||
| General Ledger | 1 | 5 | 4 | 10 | |||
| Project Accounting | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Statutory Reporting | 29 | 29 | |||||
| Total | 4 | 31 | 11 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 63 |
A further two enhancements were planned for MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements (one for Accounts Payable and one for Cost Management).
Regarding the build status of the above WRICEF’s, all have been built for MVP1.1.
The complexity of managing the MVP1.1 WRICEFs on an ongoing basis are summarised below. Appendix D details a breakdown of each WRICEF and the indicative effort required for maintenance.
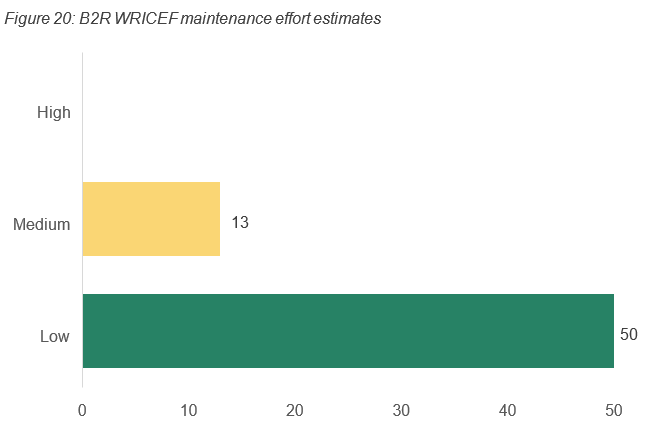
Engagement with both Services Australia and the Attorney-General Department highlighted the budgeting module was built using a top-down approach. This introduced complexities and constraints, particularly in its compatibility with the AGD established approach to budgeting. Additionally, a further 18 requirements were requested by AGD in the R2B template.
4.4.4 Revenue to Bank (R2B)
The build completion for R2B across MVP1.1 is depicted in the figure below.
Figure 22: R2B completion – full GovERP
The table below provides a detailed view of the build and testing status of respective capabilities.
Capabilities | Scope | Build Complete? see Reference 21) | Business processes | Technology component | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | MVP1.1 | No | 9 |
| Functional testing not completed for:
|
| Banking and Cash Management | MVP1.1 | No | 6 |
| Functional testing not completed for Reconcile Bank Accounts |
| Sales Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 5 | SAP S/4HANA |
4.4.5 R2B WRICEF summary
Customisations within GovERP's R2B services are quantified using WRICEF components are summarised in the table below for R2B.
Capability | Workflows | Report | Interfaces+ Integration | Conversion | Enhancement | Form | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | 1 | 2 | 10 | 13 | |||
| Banking & Cash Management | 1 | 7 | 5 | 13 | |||
| Total | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 26 |
No further WRICEF’s were planned for MVP1.1. with AGD enhancements.
Regarding the build status of the above WRICEF’s, all have been built for MVP1.1 (see Reference 23).
The complexity of managing the MVP1.1 WRICEF’s on an ongoing basis are summarised below figure. Appendix D details a breakdown of each WRICEF and the indicative effort required for maintenance.
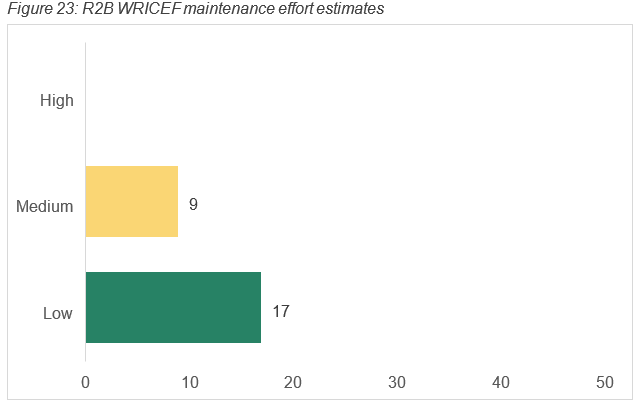
The exact and ongoing impact of maintaining these WRICEF’s will depend on the updates and releases by SAP. The release cadence for SAP S/4HANA is every 12 months.
4.4.6 Key finance insights
The key insights for Finance are summarised below:
Finance insights |
|---|
| FIN1 S/4HANA will need to be upgraded from FPS01 (2021) to at least the October 2023 build to reduce ongoing out year maintenance, and to remain on the upgrade path, noting that the underlying technical stack (Advanced Business Application Programming: ABAP) has had a version change between 2021 and 2023. |
| FIN2 38% of the processes within Finance were not agreed to by the BPMC and have not been ratified. |
| FIN3 IRAP (Infosec Registered Assessors Programme) assessment of the FMIS relied heavily on security settings in Microsoft Azure. |
| FIN4 There are 89 Finance WRICEF’s (63 in B2R and 26 in R2B), most of which will require effort to maintain. |
| FIN5 S/4HANA is the on-prem version, tenanted on the Service Australia private Microsoft Azure cloud. This version could be installed locally by another agency. |
| FIN6 Note the number of customisations and enhancements in the solution, it is likely that unless an entity has a large existing SAP workforce, that ongoing maintenance and upgrade of the solution will be difficult. Equally, for a large agency with complex ERP needs, the solution could be used as an accelerator. |
| FIN7 Consideration should be given to the integration layer that has been built during the project, it is likely the ability to integrate and pass data between other core systems and GovERP exists, and could be considered for initial data standards / integration standards. |
4.4.7 Re-use considerations for Finance
In accordance with the re-use hierarchy, each capability within Finance has been assessed for its potential for re-use. Below is a summary of all the capabilities. Note, the re-useability of Finance (i.e. B2R and R2B) has been considered holistically, given the existence of a common core platform, S/4HANA. A level of work will be required even for those listed as re-usable.
From a Tier 3, intellectual property re-use perspective, almost all information could be considered by a potential agency.
Services Australia has advised the MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements also includes enhancements that could be utilised by a whole of government instance going forward. To revert the AGD specifications but retain the remainder of the MVP1.1 template, Services Australia has estimated 60 Full Time Equivalent (FTE) days. This would result in the MVP1.1 being uplifted with enhancements that came to light during the AGD build, without the AGD specific requirements.
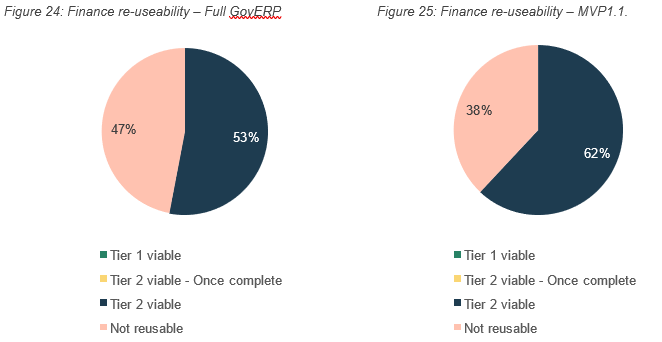
Figure 25: Finance re-useability – MVP1.1.
The table below details each capability and the potential for re-use, along with the high-level implications of doing so. Refer to section 5.2 for the adoption considerations for any agency, to assist in understanding the effort or impact involved.
Capabilities | Technology component | Re-Use Potential | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Accounting | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Budget and Planning | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Commonwealth reporting | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Cost Management | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Funds Management | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| General Ledger | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Management Reporting | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Project Accounting | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Statutory Reporting | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Tax Management | S/4HANA | Tier 2 | Maintenance Implications |
| Inventory Accounting | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Lease Accounting | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Accounts Receivable | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Banking and Cash Management | S/4HANA | Not reuseable | |
| Sales Management | S/4HANA | Not reuseable |
Whilst the table above indicates differing levels of capability reuse potential, note that Section 5 considers the pragmatic means through which an entity could consider deploying these capabilities.
4.5 Procure-to-Pay (P2P)
Procure to Pay (P2P) refers to the software and systems designed to manage and optimise the procurement and vendor management functions of an organisation within the broader framework of an ERP system.
The P2P value stream manages and supports the sourcing and purchasing of goods and services, ongoing management of the vendors and inventory, and reporting against the activities.
The FMIS S/4HANA platform is the on-prem version of the solution that delivers the P2P value stream hosted on the Microsoft Azure cloud.
4.5.1 Build status across value streams, functions, and components
The build completion for P2P for MVP1.1 is depicted in the figure below.
There were a total of 36 (see Reference 24) business processes and sub-processes which were presented to the BPMC, and all were endorsed.
Figure 27: P2P completion – MVP1.1
The table below provides a detailed view of the build and testing status of respective capabilities. Specifically, “Supplier Management” was a capability which was not in scope of MVP1.1, however, Services Australia built and tested this capability. Therefore, the MVP1.1 appears as 100 per cent incomplete, however, the Full GovERP has 8 per cent complete.
Capabilities | Scope | Build Complete? (see Reference 26) | Business processes | Technology component | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Services Procurement | MVP1.1 | Yes | 058 | SAP S/4HANA | Part of “Supplier Management” capability, so status reflects the same |
| Purchasing | MVP1.1 | No | 1 | SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement SAP SuccessFactors | Functional testing was not completed. |
| Receipting | MVP1.1 | No | 0 (see Reference 27) | SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement | Part of “Purchasing” capability, so status reflect the same |
| Contractor Management | MVP1.1 | No | 4 | SAP Success Factors SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement | Functional testing was not completed. |
| Contract Management | MVP1.1 | No | 4 | SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement | Functional testing was not completed. |
| Accounts Payable | MVP1.1 | No | 4 | SAP S/4HANA – Accounts Payable Payment Run and Approval | Below processes not built:
(via VIM) Functional testing was not completed. Note, this capability is part of the Finance business area, However, is included in the P2P value stream. |
| Report Procurement Activities | MVP1.1 | No | 4 | SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) for statutory reports AusTender Reporting Tool for AusTender reporting | Below processes not built:
Functional testing was not completed. |
| e-procurement | MVP1.1 | No | 3 | SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement OpenText Vendor Invoice Management for SAP solutions OpenText Intelligent Capture for SAP | No build information provided |
Whole of government Central Purchasing | MVP1.1 | No | 3 | SAP S/4HANA | No build information provided |
| Supplier Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | Yes (built irrespective of MVP scope) | 3 | SAP Master Data Governance | Although not in scope, the following process was built:
Functional testing did not occur. |
| Sourcing | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No (partially built irrespective of MVP scope) | 5 | SAP S/4HANA Sourcing & Procurement SAP Analytics Cloud (Reporting) SAP Master Data Governance AusTender Reporting Tool | Although not in scope, the following processes were built:
Functional testing did not occur. |
| Asset Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 5 | SAP S/4HANA | |
| Inventory Management | Not in MVP1.1 Scope | No | 3 | SAP S/4HANA |
4.5.2 P2P WRICEF summary
The table below provides a summary of these elements, detailing their presence across various P2P capabilities.
| Capability | Workflows | Report | Interfaces+ Integration | Conversion | Enhancement | Form | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | 12 | 12 | |||||
Contract Management | 2 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| Contractor Management | 1 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| Purchasing | 1 | 5 | 4 | 10 | |||
| Sourcing | 2 | 2 | |||||
| Total | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 4 | 37 |
A further eight WRICEF’s were planned for MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements which were:
- Four reports (all for Contract Management)
- Four enhancements (two for Contract Management, one for Contractor Management and one for Purchasing).
The completeness (see Reference 29) status of the WRICEFs is summarised below:
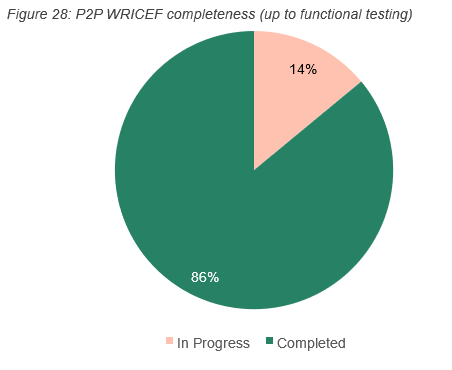
If all WRICEF’s are built, the complexity of managing the MVP1.1 WRICEFs on an ongoing basis is summarised below. Appendix D details a breakdown of each WRICEF and the indicative effort required for maintenance.
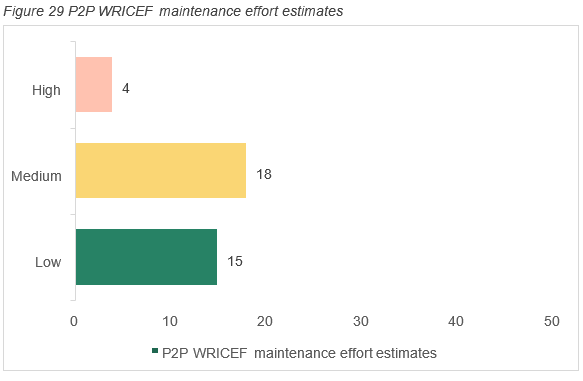
The ongoing impact of maintaining these WRICEF’s will depend on the updates and releases by SAP. The release cadence for S/4HANA is every 12 months.
Furthermore, GovERP has not integrated with either of the below whole of government solutions which are already built and operational across a range of entities:
- ARC, which is the whole of government AusTender publishing integration tool.
- Peppol, which is the whole of government e-invoicing solution.
Since comprehensive testing of procurement functionalities has not been conducted, potential vulnerabilities and defects may yet be undetected.
AGD also highlighted that it became evident the capability to be deployed was a significant step backward from their existing capability, and in some instances did not reflect the nature of procurement within the public service.
4.5.3 Key P2P insights
The key insights for P2P are summarised below:
P2P insights |
|---|
| P2P1 There are 37 P2P WRICEF’s, most of which will require effort to maintain. |
4.5.4 Re-use considerations for P2P
Based on the information provided by Services Australia regarding the build status of GovERP, it is not possible to assess the re-usability of the intended MVP1.1 build.
From a Tier 3 re-use perspective on intellectual property, almost all information could be considered by a potential agency.
4.6 Travel and Expense Management (TEMS)
Travel and Expense Management (TEMS) refers to the software and systems designed to manage and optimise the travel management and expense management functions of an organisation within the broader framework of an ERP system.
The Expense8 and GovComply products are used to deliver the TEMS value stream and are hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS). The tools are hosted onshore in either a protected (see Reference 30) or non-protected environment (see Reference 31). Build status across value streams, functions, and components.
4.6.1 Build status across value streams, functions, and components
The build completion for TEMS across the GovERP MVP and the full GovERP is depicted in the figure below.
There were a total of 27 business processes and sub-processes across four capabilities which were presented to the BPMC, and all were endorsed (see Reference 32).
Figure 31: TEMS completion – MVP1.1
The table below provides a detailed view of the build and testing status of respective capabilities.
Capabilities | Scope | Build Complete? (see Reference 34) | Business processes | Technology component | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expense Management | MVP1.1 | No | 3 | Expense8 | Functional testing not completed |
| Auditing and Compliance Management | MVP1.1 | No | 4 | GovComply | Functional testing not completed |
| Credit Card Management | MVP1.1 | No | 6 | Expense8 | Integrations for the below processes are not built:
Functional testing not completed |
| Travel Management | MVP1.1 | No | 8 | Expense8 | Integrations to SAP for the below processes are not built:
Functional testing not completed |
Although TEMS is considered not complete as advised by Services Australia, due to integrations with S/4HANA yet to occur, Reason Group have been advised by both the Department of Finance and 8common that the Expense8 product has been built and deployed within other Government Departments. Further, Expense8 has been integrated with a range of other technologies (e.g. TechnologyOne, SAP ECC6). For this reason, section 5 of this report addresses how the Expense8 product could be reused.
The GovERP template has been built into the SaaS product and is currently used by over 20 APS entities, including the Service Delivery Office in the Department of Finance and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Key functionality requested by GovERP prior to the handover to Services Australia, and which has been incorporated into the configurable SaaS product, includes:
- ‘GovComply’ which incorporated functionality capable of continuously monitoring and auditing credit card and employee reimbursements transactions. GovComply runs a series of policy tests across all transactional data on a nightly basis, creating workflow exceptions to an agency’s audit team for investigation and remediation.
- Catering for behavioural differences between official and relocation trips. Expense8 had incorporated differences in approval workflows, travel allowance calculations/rules, and available trip cost types, including 'removalist' and 'pet transportation/boarding' costs for relocation trips. Additionally, Expense8 features a configurable 'other cost' type that can be tailored to meet each agency's individual needs.
- Rebuild of the Credit Card Application Module, which now incorporates automatically inferring card limits upon application, automatically create and transmit to Diners when a new employee is added, automated deactivation of a credit card following an employee leaving, updated delegations based on APS level, and capability for an executive assistant to start a card application on behalf of their assigned executive.
- Integrated to the travel booking portal Cytric provided by Corporate Travel Management (CTM) under the whole of government travel arrangements.
4.6.2 TEMS WRICEF summary
The table below provides a summary of these elements, detailing their presence across various TEMS capabilities.
| Capability | Workflows | Report | Interfaces+ Integration | Conversion | Enhancement | Form | Total |
| Auditing and Compliance Management | |||||||
| Expense Management | 10 | 10 | |||||
| Manage Travel | |||||||
| Managing Credit Cards | |||||||
| Total | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
No further changes were planned for MVP1.1 with AGD enhancements.
The completeness (see Reference 37) status of the WRICEFs is summarised below.
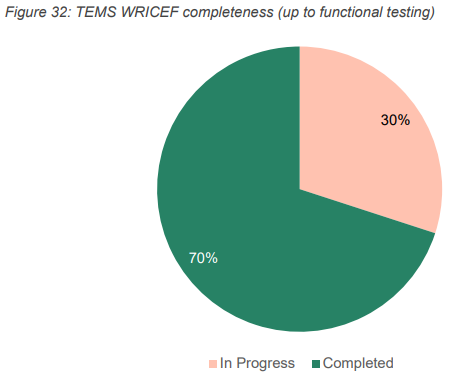
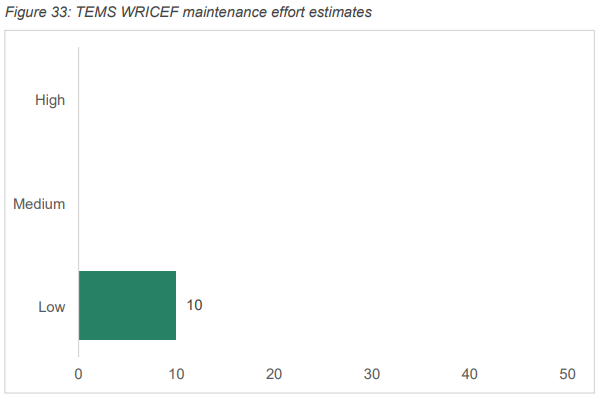
Indicatively, if all WRICEF’s are built, the complexity of managing the MVP1.1 WRICEFs on an ongoing basis is summarised below. Appendix D details a breakdown of each WRICEF and the indicative effort required for maintenance.
4.6.3 Key TEMS insights
The key insights for TEMS are summarised below.
TEMS insights |
|---|
| TEMS1 Expense8 has had several functionality uplifts prior to the handover of GovERP to Services Australia, and as a configurable SaaS product, is able to be immediately reused by other entities. |
| TEMS2 None of the WRICEFs built into the TEMS solution (Expense8 and GovComply) are anticipated to have a high complexity of ongoing maintenance. As a SaaS solution, the vendor will be responsible for the ongoing management of these WRICEFs. |
| TEMS3 There are 10 TEMS WRICEFs, all of which will require a low effort to maintain. |
| TEMS4 Despite the build status of the GovERP template for TEMS, Expense8 can be operated independently of GovERP as a standalone product, which can be integrated into another entity’s environment. |
4.6.4 Re-use considerations for TEMS
Based on the information provided by Services Australia regarding the build status of GovERP, it is not possible to assess the re-usability of the intended MVP1.1 build. The MVP test report classifies this value stream and its capabilities as either “not built” or “N/A” (see Reference 38), as they were implemented by the vendor, 8common (see Reference 39).
Note, however, the vendor, 8common, has indicated that the GovERP template is being utilised by over 40 entities including the Service Delivery Office in the Department of Finance and the Department of Veterans Affairs. The vendor has stated this template version is readily reusable as a configurable, integrable product.
The Shared Services Division of the Department of Finance has also confirmed this information.
4.7 Data
H2R provides pre-defined employee data models supporting both master data and transactional data requirements. Moreover, it offers predefined APIs for seamless interoperability and well-defined data standards.
Similarly, SAP S/4HANA Finance and Procurement solutions (B2R, R2B, P2P) presented a comprehensive set of Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) data models catering to both master and transactional data. These models were complemented by integration modules within the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) Integration Suites, exposing standardised data formats.
Customisation was introduced to align with the specific needs of the Australian Government, such as compliance with the Central Budget Management System (CBMS) and other statutory requirements.
The overarching approach to data standards embraced a blend of COTS solutions with tailored modifications to meet the requirements of the Australian government's MVP initiatives. This approach enabled alignment with the evolving landscape of governmental data exchange requirements.
During the engagement, data dictionaries were provided, explaining the structure of the data in GovERP core systems. To re-use these solutions, onboarding entities would need to adopt the data standards (and/or transform and integrate to them).
No production or personally identifiable data was loaded into GovERP, all data used in unit testing was obfuscated data (see Reference 40).
4.8 Security
4.8.1 GovERP Technology Platform
The GovERP system runs on virtual computers and storage provided by Microsoft's Azure cloud platform, managed by Service Australia (see Reference 41). This setup allows GovERP to use the processing power and resources of Azure Virtual Desktops (AVD) to run the GovERP system. This approach additionally allowed GovERP to leverage security settings established by and previously assessed for Services Australia in Azure, rather than creating a security governance model from the ground up.
All security settings were represented in the Technology Hub, which allowed administrators to manage the GovERP system and infrastructure.
Patch management via Azure Update is in place but there is no standard operating procedure. Patches for virtual machines and Microsoft applications are automatically applied via Microsoft and cannot be deferred, however timeframes were undocumented.
Backups of virtual machines and logs are configured in Azure and managed through Azure Backup. Configuration is stored as infrastructure-as-code and in Intune, both of which are backed up in Azure Backup. However, there are no formal backup procedures or processes documented for backups in GovERP.
Microsoft Sentinel was chosen as the security information event management (SIEM) solution within the Azure GTP Environment; a scalable, cloud-native, and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution.
The IRAP assessment for GTP included an assessment of the Essential Eight Strategies to Mitigate Cyber Security Incidents. The IRAP assessment of GovERP Technology Platform (GTP) relied heavily on security settings in Microsoft Azure. Multifactor Authentication (MFA) was determined to be fully met (Maturity Level 2) during the assessment; however, no other Essential Eight maturity areas were met (Level 0).
The first of several planned IRAP assessments was conducted on the GovERP stack in September 2023. This assessment relied heavily on security controls available in the PROTECTED Azure cloud, per the 2021 Azure IRAP assessment. Thus, any areas such as physical data centre, physical networking, physical hosts, virtualisation or platform management were explicitly excluded from detailed security planning as they would be inherited from Microsoft.
Identities in GovERP were to consist of unprivileged users (who use and administer the applications hosted on Azure) and privileged users who administer the underlying technology stack in Azure.
All privileged user identities were to be created in Azure Active Directory (AAD), and hence AAD was to be the GovERP platform source of truth.
AAD provided authentication and authorisation of user credentials to the hosts (Azure Virtual Desktops). Single-sign-on (SSO) to AAD resources was provided natively by Azure, however users would still be prompted for MFA or have restricted access via applications based on conditional access policies configured in the platform security design.
4.8.2 Expense8
Expense8 has had an IRAP assessment completed recently (2023), providing reasonable assurance that its security processes and maturity are suitable for government use. This assessment can be leveraged by any agency using its services.
4.8.3 SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA is a central part of the current GovERP product, integrated to other SAP components via SAP BTP. At present, S/4HANA is deployed in Services Australia private Azure tenancy.
S/4HANA has an independent security certification (IRAP/Cloud Security Assessment) which can be leveraged by other entities outside of the Services Australia tenancy. Note that the IRAP assessment focuses on the private cloud edition of SAP ERP, which may not be useful for alternative reuse strategies.
Given S/4HANA is implemented on Services Australia’s infrastructure, it will be the responsibility of Service Australia to maintain patching, upgrades, and maintenance requirements.
4.8.4 SAP SuccessFactors
SAP SuccessFactors does not assert any formal Australian government security certifications. Entities should pursue their own security certifications if using the product.
4.8.5 SAP Signavio
SAP Signavio is dedicated to modelling business processes, aiming to identify divergent processes, siloed information, and communication gaps to eliminate inefficiencies. The use of Signavio within GovERP was limited to cataloguing approved process maps, as the GovERP platform did not reach sufficient maturity to benefit from process improvement.
SAP Signavio has been IRAP-assessed (Cloud Security Assessment - March 2023) for Australian Government use, and any subsequent reuse of Signavio can leverage this assessment.
References
- Per 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024
- Services Australia, 220707.5.01 AttA GovERP End to End Solution Architecture v2.0, Section 8.1.1. ‘Technology Decisions and Architecture Alignment, July 2022
- 1. 220623.5.04 AttA Finance HLA v1.0, page 73
- There is a known disparity between the number of process maps approved and the number of process maps included in Decision 22 as per the ‘Business Process’ column within the below build and functional testing status table. The exact reason for this disparity could not be prosecuted as part of this assessment, as the BPMC minutes and meeting content, which included the process maps, was unable to be provisioned by Services Australia in time for this report.
- As per 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024.
- Results extracted from 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024.
- The presence of these WRICEF components for a capability indicates that custom developments or configurations are in place. WRICEF components and changes to the core via enhancements add consideration to the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of capabilities in GovERP (see Reference X).
- As per 220707.5.01 AttA GovERP End to End Solution Architecture v2.0, July 2022
- Completeness refers to the completion of both build and functional testing.
- As per Request #6 - Responses to clarification questions 1604 v1.0
- Refer to Section 2.4.3 Potential for reuse
- Per 220609.5.01 AttA GovERP Application Landscape Strategy V2.0.pdf, June 2022
- There is a known disparity between the number of process maps approved and the number of process maps included in Decision 22 as per the ‘Business Process’ column within the below build and functional testing status table. The exact reason for this disparity could not be prosecuted as part of this assessment, as the BPMC minutes and meeting content, which included the process maps, was unable to be provisioned by Services Australia in time for this report.
- Per presentation DTA Reuse Meeting 3 April 2024 redacted, April 2024
- As per 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024.
- Results extracted from 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024.
- As per Request #6b - Updated 1804 - final responses to clarification questions 1604 v1.1
- As per Request #6b - Updated 1804 - final responses to clarification questions 1604 v1.1
- The presence of these WRICEF components for a capability indicates that custom developments or configurations are in place. WRICEF components and changes to the core via enhancements add consideration to the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of capabilities in GovERP.
- As per ‘17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial’.
- Results extracted from 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial.
- The presence of these WRICEF components for a capability indicates that custom developments or configurations are in place. WRICEF components and changes to the core via enhancements add consideration to the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of capabilities in GovERP.
- Completeness refers to the completion of both build and functional testing.
- There is a known disparity between the number of process maps approved and the number of process maps included in Decision 22 as per the ‘Business Process’ column within the below build and functional testing status table. The exact reason for this disparity could not be prosecuted as part of this assessment, as the BPMC minutes and meeting content, which included the process maps, was unable to be provisioned by Services Australia in time for this report.
- As per 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial.
- Results extracted from 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial
- Processes for this capability were rolled into “Purchasing” per Decision 22 found in Decision Framework Briefing_Outcomes of SSSC, page 145.
- The presence of these WRICEF components for a capability indicates that custom developments or configurations are in place. WRICEF components and changes to the core via enhancements add consideration to the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of capabilities in GovERP.
- Completeness refers to the completion of both build and functional testing.
- Only accessible onshore with relevant security clearances.
- Overseas support can be provided on the non-protected environment.
- There is a known disparity between the number of process maps approved and the number of process maps included in Decision 22 as per the ‘Business Process’ column within the below build and functional testing status table. The exact reason for this disparity could not be prosecuted as part of this assessment, as the BPMC minutes and meeting content, which included the process maps, was unable to be provisioned by Services Australia in time for this report.
- As per 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial, April 2024.
- Results extracted from 17. 20240410 GovERP MVP WoAG Template status v1.2 Baseline + Updated with comments for Partial.
- 8common advised verbally that this integration occurred after the pause of GovERP, however, this was not validated in the information provided by Services Australia.
- The presence of these WRICEF components for a capability indicates that custom developments or configurations are in place. WRICEF components and changes to the core via enhancements add consideration to the maintenance overhead associated with these customisations when assessing the reusability of capabilities in GovERP.
- Completeness refers to the completion of both build and functional testing.
- Meaning not applicable
- As per 26. GovERP Template Test Execution Summary Report, page 2
- As per advice received from Services Australia. Note, Reason Group did not cite the data included within GovERP.
- As per GovERP Technology Platform (GTP) IRAP Assessment v1.3 2023

