-
Investment by sector
This section explores the projects underway across the Australian Government through a ‘sector’ lens.
Number of projects and total budget by sector
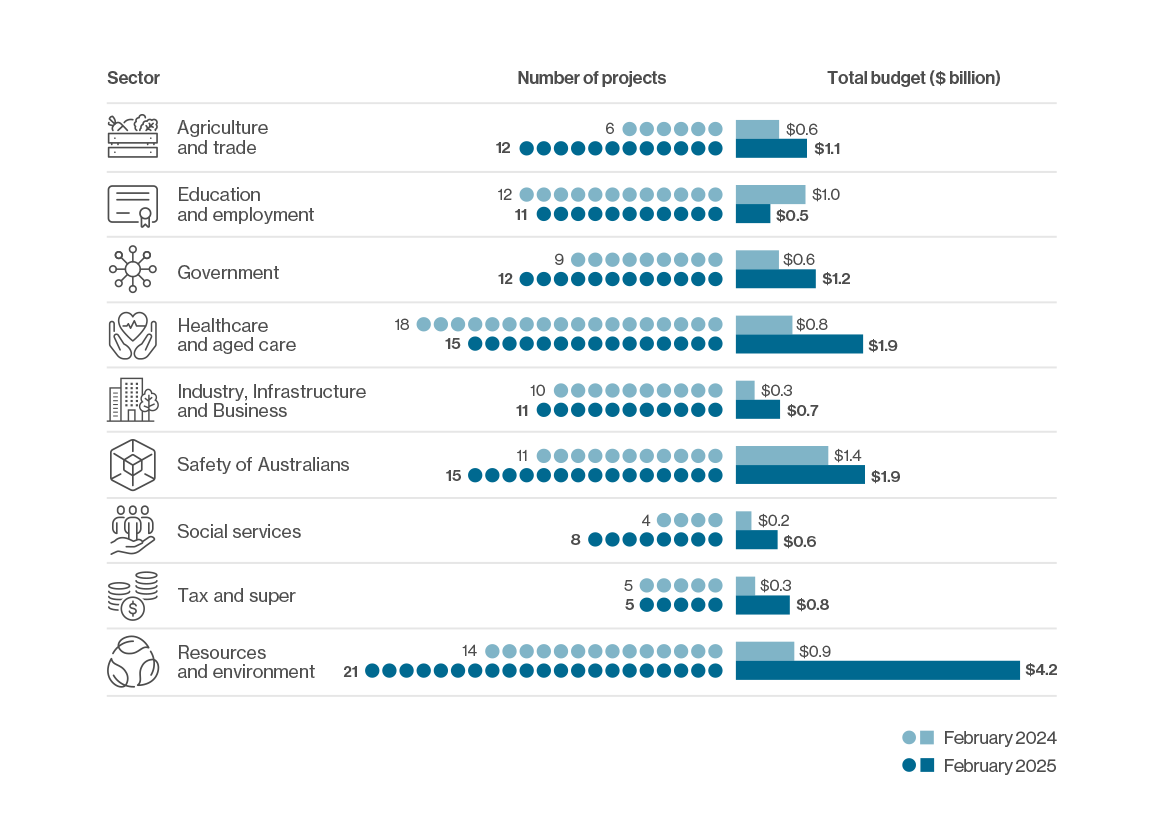
Digital projects under the DTA’s assurance oversight are improving systems and services across 9 sectors. A common thread across all sectors is investment to improve agency systems to meet digital standards and enable them to provide simple, secure and seamless services to Australians.
Project numbers and budgets have increased in most sectors.
-
Image description
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Appendix
-
Image description and download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Delivery confidence and duration of closed projects
Finishing up – how projects leaving the portfolio performed
-
Image description
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Of the 13 Tier 1 and Tier 2 projects that closed, 10 (76.9%) reported a High or Medium-High delivery confidence. Just 2 projects had a rating of Medium or lower, while one project did not report a delivery confidence rating.
Between February 2024 and February 2025, and before closing, 4 of these projects improved their delivery confidence, and 3 projects stayed the same. Comparisons for the remaining projects are not possible as they did not report a delivery confidence in February 2024.
The average duration of closed projects was 2.5 years. Closed Tier 1 projects had a longer average duration than Tier 2 and Tier 3 projects. This longer average duration is mainly due to the inclusion of a closed 7-year Tier 1 project to improve weather and climate data.
Challenges and lessons learned
Projects that closed since February 2024 generally reported underspends. Those that went over budget reported issues including initial scoping not accounting for the full complexity of required work.
Some projects faced challenges in their ability to deliver against their original schedule due to delays getting bills introduced to Parliament, delays with equipment supply due to the COVID-19 pandemic, post-release issues that needed to be addressed, and additional enhancements that needed to be delivered to achieve expected outcomes.
Common lessons learned include:
- allocating sufficient time to early planning pre-implementation (preparation) stages, including ensuring a deep understanding of current state processes
- developing collaborative working relationships between stakeholders during scoping, delivery planning and decision-making – including efficient knowledge transfer and upskilling as needed
- defining project scope in as much detail as possible, to avoid confusion in deliverables and align project outcomes with stakeholder expectations
- enhancing financial management and budget control – including to enable tracking of earned value during implementation.
The importance of closure reports
Formal closure of a project is more than just the project finishing. Driving improved project performance over time requires careful consideration of how in-flight projects have performed, and how what we’ve learned should change the way projects are designed and delivered in future. Strengthened central oversight has this ‘system learning’ at its centre with the DTA ensuring lessons aren’t just identified but rather systematically learned across all major digital projects through real change which makes the difference.
Project closure reports play a vital role in this ‘system learning’ and, as closure reports have varied in quality, a closure reporting standard has been developed to ensure consistency and maximise the value of these reports.
Improving project closure reports
To formally close a project, agencies must provide a project closure report to all key stakeholders. However, some reports have included extensive information, requiring more resources than necessary, while others have provided insufficient information to accurately assess the project’s performance.
As a result, the DTA developed the Closure Reporting Standard for Digital and ICT-enabled projects. The standard provides a minimum and consistent set of information for reports based on 7 criteria – scope, schedule, budget, assurance, benefits realisation, transition arrangements, and lessons learned. By standardising closure reporting, the DTA is promoting best practice and providing the necessary information to evaluate completed projects and inform future investments.
We are drawing on expertise from across the APS and working with the Australian Taxation Office to develop templates to support implementation of the standard.
-
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Project numbers and value
Since February 2024, the resources and environment sector experienced a net increase of 7 projects and $3.4 billion growth in investment. This is largely attributed to one 35 year-long project that intends to secure the resources needed for Australia’s transition to net-zero. The government sector experienced a net growth of $0.5 billion, largely related to investment in Australia’s 19th national Census and the replacement of legacy systems to modernise Australia’s electoral systems.
Despite a reduced number of projects, the healthcare and aged care sector grew by $1.1 billion in value. This reflects investment in projects to support new vaping reform legislation, a range of COVID-19 outbreak management supports, and improvements to Australia’s healthcare settings, platforms and systems.
Delivery confidence
The agriculture and trade sector and the industry, infrastructure and business sector have the largest proportion of Tier 2 projects reporting a delivery confidence of Medium-High and higher. Most projects within these sectors are reporting as on track to deliver expected benefits.
The healthcare and aged care sector has the equal largest proportion of Tier 1 projects reporting a delivery confidence of Medium or lower. This is mainly due to capacity and legislative constraints. The DTA is working closely with the Department of Health and Aged Care to support the successful delivery of investments in this area – including by carefully managing pacing of new investment where it could compete with an already crowded delivery schedule.
The safety of Australians sector has the largest proportion of Tier 2 projects reporting a delivery confidence of Medium and lower. Technical constraints, resourcing and funding pressures are contributing to delivery stress within this sector.
It will remain challenging to secure a skilled workforce. Agencies will need to invest in new approaches to build capability in areas experiencing skill shortages. When planning and scheduling digital investments, it is crucial to account for the capabilities required to ensure projects have sufficient resources to deliver.
Across all sectors, digital projects can prove challenging to deliver successfully – but they remain critical to enable policy reforms designed to improve and even save the lives of Australians.
Healthcare and aged care
Digital services are improving the health of Australians, including the care of older people. The 15 active projects in this sector, with a combined value of $1.9 billion, reflect the recent increase in government investment in this area.
Most of the funding ($1.3 billion) is for 9 projects to improve the aged care sector by implementing recommendations following the Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety in 2021. This includes:
- improving ICT capabilities of federal agencies to enable more effective regulation of the aged care industry
- delivering a modernised system that supports aged care service providers to provide the high quality, safe care that older people deserve
- ensuring nurses are available at all residential care facilities and all aged care workers are registered on a national register
- supporting the different levels of independence and care required by older Australians.
The remaining 6 projects ($0.6 billion) are delivering new and improved health services, completing digital transformation of internal systems, and producing better online portals for Australians to access services.
Safety of Australians
The government is protecting vulnerable Australians by investing in law enforcement and online safety through 15 active projects with a combined value of $1.9 billion, being delivered across 11 Commonwealth agencies.
These projects are safeguarding Australia by:
- improving access to cross-border information and real-time risk data on dangerous individuals and organisations
- enhancing data matching capability to reduce investigation time and improve the ability to combat organised crime
- contributing to a national view of policing information and criminal intelligence
- using machine learning and artificial intelligence to significantly improve Australia’s efforts to combat illicit activities such as money laundering and unauthorised imports
- developing comprehensive registries and data lakes to store historical information to allow authorities to identify suspicious activity faster
- automating border clearance and cargo processes to simplify government services while also improving security alerts and risk information.
Other investments are improving the use of data to combat the growing threat of scams targeting Australians (see[GC1] case study on page xx), protecting myGov users by strengthened measures to prevent phishing attacks (see case study on page xx) and targeting disability insurance fraud (see case study on page xx).
Resources and the environment
The government is investing $4.2 billion into 21 projects to help protect and restore Australia’s vast and varied environment and manage the country’s natural resources.
This includes a long-term project ($3.4 billion) to comprehensively map Australia’s natural resources, including critical minerals and groundwater, to support the transition to net zero and enable responsible management of all resources. Another project (over $104 million) is helping to improve the management of water resources and responses to climate change impacts in the Murray-Daring Basin.
Another 8 projects (over $535 million) are leveraging data and technology to enable rapid action to address environmental changes. Data, information and analytics are being used to better manage and protect Australia’s natural heritage and streamline work on environmental and climate risk assessment projects. Significant investment is also supporting emissions reduction and renewable energy mechanisms.
A further 5 projects (over $104 million) are building the skills and data infrastructure needed to manage and monitor energy, water and diesel exhaust fluid markets and plan for future supply and demand.
A previous investment in this sector, which concluded in June 2024, modernised and secured critical climate and weather data services (see case study on page xx).
[GC1]For webpage view hyperlink to relevant case study pages where highlighted yellow
-
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Education and employment
Education and employment underpin achievement and prosperity in Australia. The government is investing $512.5 million across 11 projects to reform this sector by removing barriers, enhancing outcomes and creating more efficient processes.
Digital projects in this sector are using digital tools to enhance childcare subsidy administration, automate workflows, back up records, and connect service providers – improving quality and capacity.
Student loans enable further education in Australia. Initiatives are enhancing data quality and insights through organised information storage and automated processes and supporting more effective distribution of resources and a more efficient student loans system through integration of data.
Projects related to employment services are simplifying the user experience and reducing system strain. Centralised data management is enabling effective tracking of employment trends, driving data-driven improvements. Consolidating services onto a single platform will enhance outcomes and reduce operational costs.
The modernisation of Australia’s vocational education management system aims to expand the workforce. Initiatives are overhauling the administration of VET Student Loans and replacing outdated systems, which is essential to upscale apprenticeship programs and services.
Tax and super
An efficient tax and superannuation system aims to reduce unnecessary costs on the economy, while raising revenue to fund critical government services. The government is investing in 5 major projects in this sector, with a combined value of $803.4 million.
One project in this sector is helping to safeguard workers’ entitlements and address the systemic issue of employers not paying or underpaying Superannuation Guarantee entitlements. Another project is improving data availability and access to tools to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of Australian Taxation Office (ATO) staff. This will enable enhanced data matching to minimise the need for staff to manually identify unpaid Superannuation Guarantee entitlements, while also reducing the reporting burden for employers.
Investment in new ATO systems has streamlined the process of managing tax requirements. Reforms to enhance the robustness, equity and sustainability of the retirement savings system are also being supported through digital projects, benefiting a broader range of Australians and supporting retirees. Other initiatives are enhancing the ATO’s capability to defend against cyber attacks, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and availability of internal systems and data.
Another project is making sure the ATO can meet the ICT and data requirements to support a global initiative to tackle multinational tax avoidance.
Some of the technological foundations for such projects within the tax and super sector were laid through a previous ATO data centre project (see case study on page xx).
Industry, infrastructure and business
A primary role of government is improving quality of life for Australians through investing in domestic productivity. To this end, the government is investing $657.9 million across 11 projects in the industry, infrastructure and business sector. Projects are:
- enhancing business interactions with government by automating and simplifying processes to reduce time and complexity
- improving reporting processes to meet community standards of transparency and fairness, which benefits business tenders
- enhancing cyber security, functionality and operational sustainability to enable the Australian Government to regulate, support and oversee domestic businesses – promoting economic growth and transparency
- addressing gaps in existing processes, ensuring timely payments to small businesses and grants to states and territories, and simplifying engagements between government and small to medium enterprises.
Further, geospatial digital projects are improving diverse areas like climate reporting, water, geography and demographics. Collaboration with overseas partners is boosting Australian research in climate change, clean energy and agricultural productivity. A partnership with the United States is leveraging expertise in the crucial area of satellite data. Enhancing ICT capabilities to support Australian science and foreign affairs management is paving the way for future business and employment opportunities.
-
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Agriculture and trade
Agriculture and trade are essential to the Australian economy. To create the right support for the sector, the government is investing in 12 projects with a value of $1.1 billion to transform import and export processes.
Various agencies are making digital improvements, integrating machine learning into existing processes and developing platforms to support digital verification of trade documents.
A digitisation initiative is modernising Australia’s agricultural export systems. Streamlining existing processes will alleviate administrative and operational burdens for businesses and reduce the costs associated with exporting goods.
Other projects are ensuring compliance with a complex network of international obligations through enhanced information sharing and simplified system interactions. Initiatives are supporting Australia’s international trade, cooperation and regulatory missions by enhancing security and functionality to enable secure, flexible and scalable business operations. This will improve interconnectivity across agencies and create flexibility to implement new programs, while maintaining the security advantages of an enclosed system.
-
Image description and file download
PLACEHOLDER
Off -
-
-
Social services
The social services sector plays a crucial role in supporting the wellbeing of Australians. The government is investing $621.3 million across 8 projects in this sector to modernise the delivery of social services, ensuring they are more efficient, accessible and better aligned to the needs of Australians.
Important initiative to improve outcomes for people with disability include:
- bringing together de-identified data from the Australian, state and territory governments to enable a better understanding of the life experiences and outcomes of people with a disability across Australia
- better supporting people with disabilities in securing employment
- improving capability to protect people with disabilities from abuse, violence, neglect and fraud.
Another project is transforming how Australians access government services by providing a secure and efficient way for individuals to verify their identity online.
Further significant investments are modernising digital services to support veterans, streamlining the claims administration process and ensuring timely delivery of payments to assist veterans and their families.
Government
For the Australian Government to fulfill its commitment to delivering value through its digital and ICT‑enabled projects, it needs to have robust internal processes and systems to support its operations. To support this, a total of $1.2 billion has been invested in the government sector across 12 projects.
Modernised systems are crucial for the APS to effectively and efficiently manage its responsibilities. They are needed to ensure Commonwealth agencies comply with cyber security policies, minimise vulnerabilities and can protect sensitive information from potential attacks.
Current digital architecture and ageing technology cannot support increased demand or maintain compliance.
ICT capability projects range from work to support election services to national data collection, and are:
- enhancing cyber security and reliability across several Commonwealth agencies, reducing shared cyber risks and aligning with government policies
- upgrading systems to meet digital standards, enhance service delivery, reduce errors and increase efficiency
- ensuring the integrity of collected data to lead to more comprehensive insights supporting the development of policy and distribution of funds and services.
Across all sectors, consistent quality and timeliness of reporting to project decision-making bodies is essential for effective decision-making. To support this, the DTA is trialling a new standard for project data reporting. The trial aims to enhance the quality, consistency, and visibility of critical project information, ensuring that decision-making bodies have the necessary information for effective decisions.
-
Glossary of acronyms, abbreviations and terms
Term/acronym Definition ACCC Australian Competition and Consumer Commission API Application Programming Interface API Gateway A tool that manages and optimizes API traffic. APS Australian Public Service Artificial intelligence A machine-based system that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or virtual environments. Different AI systems vary in their levels of autonomy and adaptiveness after deployment. ASIC Australian Securities and Investments Commission Assurance Framework Assurance Framework for Digital and ICT Investments ATO Australian Taxation Office Business case A document outlining the justifications for funding and commencement of a government project. CDoF Crack Down on Fraud CEO Chief Executive Officer Corporate Commonwealth Entities A body corporate that is legally distinct from the Commonwealth and can exercise legal rights including entering contracts and owning property. Cryptographic keypair technology A security technology using a public encryption key and a private decryption key pair. Data lakes A centralised storage system for large amounts of raw or unprocessed data. DCA Delivery Confidence Assessment DCAP Digital Capability Assessment Process De-identified Data that has been removed of any identifying information, making it impossible to identify the person it was originally associated with. Delivery confidence A snapshot assessment based on available governance, resource management, delivery management, solution design, business case and other evidence to approximate the overall likelihood of a digital project to deliver expected benefits for Australians on time and on budget. Diesel exhaust fluid A liquid used to reduce the amount of air pollution created by a diesel engine. Digital ID Digital Identification Digital projects An investment of government funds into the purchasing or development of digital or ICT technologies as part of a larger project or on its own. Digital transformation Integration of modern digital and ICT technologies into government processes and services. Discovery work Activities undertaken to explore, validate and define what needs to be built before committing to development. DTA Digital Transformation Agency Enclosed system A security and data system that is isolated from the internet and external environment which prevents data entering and leaving. FFT Fraud Fusion Taskforce Gateway review An additional assurance practice to assist non-corporate Commonwealth entities to successfully deliver high risk projects and programs. Geospatial digital projects Use geospatial data to create digital models of the physical world. ICT Information and Communication Technology IIAP ICT Investment Approval Process Integrated data platforms A system that collects, integrates, and analyses data from multiple sources. Machine learning A type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate in predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed. MYEFO Mid-Year Economic and Fiscal Outlook NASC National Anti-Scam Centre NDIA National Disability Insurance Agency NDIS National Disability Insurance Scheme NMI National Measurement Institute PDRS Project Data Reporting Standard Product/service enhancement investments Improve the operations of an existing product or service. RAP Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity Initiative SFIA Skills Framework for the Information Age SRO Senior Responsible Official Superannuation guarantee The minimum amount of superannuation paid to employees by their employer. Sustainment investments Sustainment involves the provision of in-service support, including repair and maintenance, engineering, supply and replacement parts, configuration management and disposal action. Technical debt The cost of future work that results from choosing a quick solution over a more efficient one. Tranche A group of smaller related objectives or actions that are delivered as part of a larger project. Often Tranche 1 establishes processes and supports required for further Tranches to be delivered. VET Vocational Education and Training WELD Waste Exports Licencing and Declaration
Connect with the digital community
Share, build or learn digital experience and skills with training and events, and collaborate with peers across government.

